Page 7 - 2021 Spring CMTA Report - Special Research Edition
P. 7
Cross-Type Initiatives While there are many genetic causes of CMT, certain advancements are common to virtually all types.
Those commonalities include the development of gene therapies, improving genetic
diagnostics and extending it to currently unclassified types of CMT, providing the biomarkers that enable
and stimulate clinical trials, preventing axon degeneration and developing inhibitors.
EFFICIENT, EFFECTIVE themselves are not sensitive enough There are nerves present in the skin,
BIOMARKERS CRITICAL to changes and therefore not really so the affected Schwann cells—
adequate to serve in a clinical trial as
the cells in the peripheral nervous
FOR CLINICAL TRIALS a measure of whether the neuropathy system that produce the myelin
Because clinical trials involve a large has improved. sheath around neuronal axons—
investment of both time and funding, can be assessed by sensitive gene
many conversations with CMT Biomarker efforts extend across types detection methods to determine the
pharmaceutical partners about and include a number of different level of PMP22.
potential therapies focus on how to studies. In London, neurologist
design clinical trials that will quickly Dr. Mary Reilly developed a biomarker GENE DISCOVERY
address a new medication’s efficacy. that uses magnetic resonance Gene discovery is another area the
imaging (MRI) to measure the amount
These companies want to see of muscle mass in calves. As CMT CMTA is pursuing. Fewer than 50
measures that can evaluate signs of progresses, there is a gradual percent of CMT Type 2 patients know
success, ideally within three to six replacement of some of the muscle their gene. If the gene isn’t known,
months of starting the clinical trial. with fat. MRI was not identified with there can be no therapy development
A measure that works only after a year CMTA support, but we are supporting and the patient is likely to be forced
or two simply takes too long for extension of 1A studies to other types. into an ongoing “diagnostic odyssey.”
them to make that investment. The CMTA supports the most
Consequently, one of the most urgent Dr. Reilly and Dr. Alexander Rossor important genomic initiative by the
needs in the CMT field is to find also found that blood samples can INC and the GENESIS project, which
better ways to assess the dysfunction be used to measure a protein called in 2020 discovered the most common
of the peripheral nerves in patients neurofilament light that is released recessive CMT2 gene–SORD
with CMT. from CMT nerves. Since the focus of neuropathy, which may be treatable
several CMT1A therapies is reducing
The CMTA was an early supporter the expression of the PMP22 gene with already-approved drugs. The
of INC’s development of neuropathy that causes neuropathy, the majority of CMT genes have been
scores for adults. They went on collaboration of Dr. Michael Shy at discovered in the past decade in
to develop pediatric and infant the University of Iowa and Dr. John this effort.
neuropathy assessments. But since Svaren at the University of Wisconsin
CMT is a slowly progressive disease, has turned to the analysis of both
these neuropathy scores by blood samples and skin biopsies.
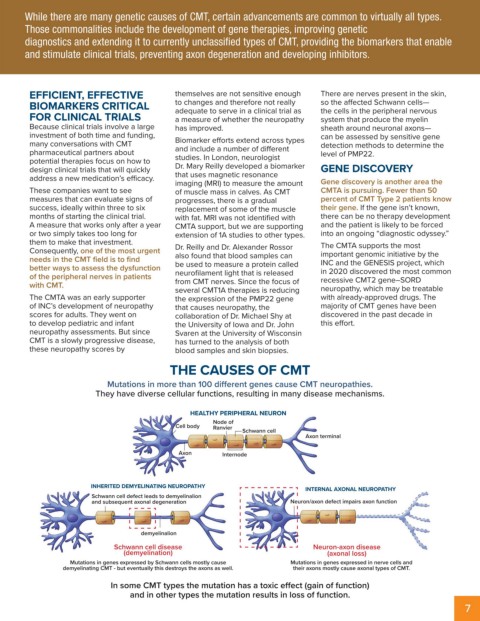
THE CAUSES OF CMT
Mutations in more than 100 different genes cause CMT neuropathies.
They have diverse cellular functions, resulting in many disease mechanisms.
HEALTHY PERIPHERAL NEURON
Node of
Cell body Ranvier Schwann cell
Axon terminal
Axon Internode
INHERITED DEMYELINATING NEUROPATHY INTERNAL AXONAL NEUROPATHY
Schwann cell defect leads to demyelinalion
and subsequent axonal degeneration Neuron/axon defect impairs axon function
demyelinalion
Schwann cell disease Neuron-axon disease
(demyelination) (axonal loss)
Mutations in genes expressed by Schwann cells mostly cause Mutations in genes expressed in nerve cells and
demyelinating CMT - but eventually this destroys the axons as well. their axons mostly cause axonal types of CMT.
In some CMT types the mutation has a toxic effect (gain of function)
and in other types the mutation results in loss of function.
7